Rebar spacing guidelines generally require bars to be placed between 5 inches and 15 inches apart. This spacing is crucial for structural integrity and load distribution.
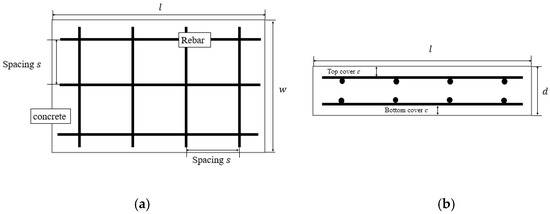
Understanding rebar spacing is essential for anyone involved in the construction or renovation of concrete structures. Rebar, or reinforcing bar, plays a pivotal role in enhancing the tensile strength of concrete, making it indispensable in modern construction projects. The guidelines for rebar spacing ensure that concrete elements, such as floors, walls, and beams, can withstand various loads and stresses over time.
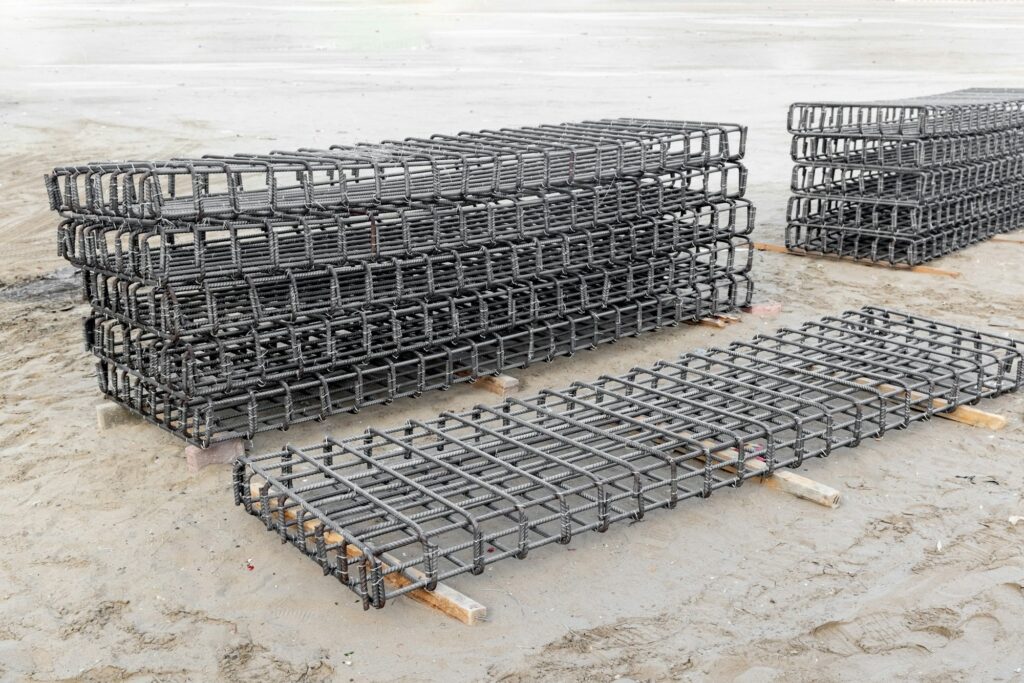

Adhering to these specifications not only guarantees safety but also contributes to the longevity and durability of a structure. Proper rebar spacing is determined by factors such as the load requirements, the size of the rebar, and the specific application in construction. This guide aims to provide a clear understanding of how to effectively implement rebar spacing in your next project, ensuring structural efficiency and compliance with building codes.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Introduction To Rebar In Construction
Introduction to Rebar in Construction dives into the backbone of modern buildings and structures. Rebar, short for reinforcing bar, strengthens concrete in construction projects. This introduction explores rebar’s role and why its spacing matters.
Role Of Rebar In Concrete Structures
Concrete is strong under compression but weak when pulled apart. Rebar, made of steel, helps by handling the tension. It makes concrete structures like bridges, roads, and buildings much stronger. Think of rebar as the skeleton that supports and holds the concrete body together.
- Supports the concrete under tension
- Prevents cracks from spreading
- Increases the lifespan of structures
Importance Of Proper Rebar Spacing
Placing the rebar correctly is crucial. It ensures buildings and bridges are safe and durable. Proper spacing prevents cracks and structural failures. It’s not just about strength but also about safety and longevity.
| Structure Type | Recommended Spacing |
|---|---|
| Walls | 12 to 16 inches |
| Floors | 8 to 12 inches |
| Foundations | 4 to 8 inches |
Correct spacing ensures each rebar piece works together. It helps the structure handle loads and stresses over time. Too close, and concrete might not cover rebar well. Too far apart, and the concrete might crack. Finding the right balance is key.
Basics Of Rebar Spacing
Understanding the basics of rebar spacing is critical in construction. Proper rebar spacing ensures stability and strength in concrete structures. It prevents cracks and structural failures. Let’s explore the standard sizes and grades of rebar, and the factors that affect its placement.
Standard Rebar Sizes And Grades
Rebars come in various sizes and grades. Each size and grade has specific uses in construction. Common sizes range from #3 to #11. Grades signify the rebar’s yield strength. For example, Grade 60 rebar can withstand 60,000 psi.
Add more rows as needed
| Rebar Size (Number) | Diameter (Inches) | Grade |
|---|---|---|
| #3 | 8 | B 420 & B 500 |
| # | 10 | B 420 & B 500 |
| #5 | 1 | B 420 & B 500 |
| #6 | 16 | B 420 & B 500 |
Factors Influencing Rebar Placement
- Concrete cover: This is the rebar’s protective layer. It guards against corrosion and fire.
- Load requirements: Buildings have different load needs. Rebar spacing varies with these needs.
- Local building codes: Codes can dictate rebar size, type, and spacing. Always check local regulations.
- Environmental factors: Weather and soil conditions influence rebar spacing. Professionals consider these before placement.
Correct rebar spacing is vital for safe and durable structures. Always consult with an engineer for precise guidelines.
Codes And Regulations
Building codes and regulations set the standard for rebar spacing.
These ensure safety and structural integrity. Professionals must adhere to these guidelines.
Building Codes Impacting Rebar Spacing
Local building codes dictate rebar spacing. These codes vary by region and purpose.
Builders consult these codes before construction.
- Codes prevent structural failures.
- They ensure uniform practices.
- Spacing affects load-bearing capacity.
Code compliance is mandatory. Inspectors check rebar spacing during construction.
International Standards For Rebar Spacing
International standards guide global practices. They help in maintaining consistency.
| Standard | Purpose | Spacing Guidelines |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 6935-2 | Steel for reinforcement | Defines characteristics |
| ASTM A615 | Rebar specifications | Details size, grade, spacing |
Builders worldwide follow these standards. They ensure structures stand strong.
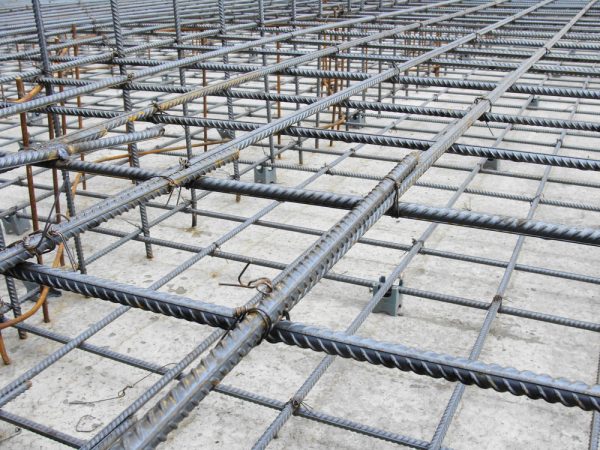

Credit: matmatch.com
Calculating Optimal Rebar Spacing
Rebar spacing is crucial in construction. It ensures stability and strength in concrete structures. Correct calculations prevent future cracks and failures. Let’s discuss how to calculate the best spacing.
Tools And Software For Rebar Calculation
Different tools and software help with rebar calculations. They ensure accuracy and save time. Here are some commonly used ones:
- Rebar calculator apps: Quick estimates on-the-go.
- Spreadsheet programs: Customizable for complex projects.
- CAD software: Detailed visuals alongside calculations.
Examples Of Rebar Spacing Calculations
Let’s look at some rebar spacing examples. Remember, local building codes guide these numbers.
| Project Type | Rebar Size | Spacing |
|---|---|---|
| Walls | #4 Bars | 16 inches |
| Floors | #5 Bars | 12 inches |
| Foundations | #6 Bars | 8 inches |
These examples show common practices. Always check codes for your specific project.
Common Rebar Spacing Mistakes
Understanding rebar spacing is crucial in construction. Mistakes can lead to structural failures. Builders must follow guidelines to ensure stability and durability. Here are common errors:
- Ignoring load requirements
- Choosing the wrong rebar size
- Overlooking concrete cover
- Failing to consider environmental factors
Consequences Of Incorrect Spacing
Poor rebar spacing can lead to serious issues:
| Consequence | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced strength | Compromises load-bearing capacity |
| Cracking | Leads to early deterioration |
| Corrosion | Shortens the structure’s lifespan |
Case Studies: Lessons Learned From Failures
Real-world examples show the importance of proper spacing:
- Bridge Collapse: Inadequate rebar spacing led to a tragic failure.
- Building Crack: Incorrect spacing caused extensive and costly repairs.
- Parking Garage: Skipped guidelines resulted in a complete rebuild.
Each case underlines the need for strict adherence to rebar spacing rules.
Best Practices For Rebar Spacing
Understanding Best Practices for Rebar Spacing is crucial for strong structures. Correct spacing ensures durability and safety. It supports loads and withstands various stresses.
Tips From Industry Experts
Follow these expert tips for optimal rebar spacing:
- Use minimum spacing as per the American Concrete Institute (ACI) guidelines.
- Avoid too close spacing to prevent concrete cracking.
- Consider rebar size to determine proper spacing.
- Ensure even distribution across the concrete slab.
- Check local codes for specific spacing requirements.
Innovations In Rebar Installation Techniques
New tools and methods improve rebar installation:
- Magnetic positioning systems ensure precise spacing.
- Fiberglass rebar offers easier handling and installation.
- Software for planning helps visualize spacing and distribution.
- Robotic installation aids in large projects for consistency.
Embrace these innovations for efficient and reliable rebar setups.
Inspecting And Adjusting Rebar Spacing
Inspecting and adjusting rebar spacing is crucial for construction integrity. Correct spacing ensures stability and strength in concrete structures. Inspectors and construction teams must follow strict guidelines. These ensure the longevity and safety of the built environment.
Quality Assurance Procedures
Quality assurance is key for rebar placement. Regular checks confirm correct distances between bars. Procedures include:
- Visual Inspections: Experts look at rebar arrangements. They ensure compliance with design specifications.
- Measurements: Tools measure spacing. This verifies consistency throughout the structure.
- Documentation: Records keep track of inspections. This helps identify any potential issues early.
Adjustment Strategies During Construction
Adjustments might be necessary during construction. Strategies include:
- Immediate Corrections: Workers fix spacing issues as they’re found. This prevents future problems.
- Rebar Ties: Ties secure bars in the correct position. They prevent movement during concrete pouring.
- Communication: Teams discuss findings. They make adjustments in real-time.
Following these strategies ensures structures meet design and safety standards.
Future Trends In Rebar Usage
Rebar is essential in construction. It strengthens concrete structures. Experts are now exploring new trends in rebar usage. These trends will change construction. Let’s explore these future trends.
Advancements In Material Science
New materials make rebar stronger and lighter. Scientists create rebar that resists corrosion better. This reduces maintenance costs. Composite materials are now in use. They combine strength with flexibility. These materials include carbon fiber and basalt fiber. They are changing how we use rebar.
Evolving Standards And Building Techniques
Building codes change with new knowledge. They now demand safer, more sustainable structures. Construction methods evolve too. Builders use 3D printing and prefabrication. These methods need different rebar spacing. They improve speed and efficiency. Smart rebars with sensors are also in development. They monitor the health of structures. This information helps maintain bridges and buildings better.
Rebar spacing guidelines are crucial. They ensure safety and durability. The future will bring smarter, more adaptive rebar usage. These trends will redefine rebar spacing. They will make buildings last longer and safer.

Credit: support.tekla.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Far Apart Should Rebar Be Placed?
Rebar spacing typically ranges from 4 to 18 inches, depending on the project’s structural requirements and local building codes. Always consult relevant guidelines to ensure proper distance and support.
What Is The Code For Rebar Spacing?
Rebar spacing codes vary by region, but generally follow ACI (American Concrete Institute) standards. Check local building codes for specific requirements.
What Is The Minimum Spacing Between Rebars?
The minimum spacing between rebars typically depends on the local building codes but generally is at least 1. 5 times the diameter of the rebar used. This ensures proper concrete flow and structural integrity. Always check specific regulations for your project.
How Far Apart Should Rebar Layers Be Spaced?
Rebar layers should be spaced 12 to 18 inches apart for optimal strength and stability. This spacing ensures proper concrete coverage and load distribution. Always consult specific project requirements for best results.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of rebar spacing is crucial for structural integrity. By embracing the guidelines we’ve explored, you’ll ensure your construction projects stand firm against stress and time. Remember, precise spacing is not just a recommendation; it’s a cornerstone of safe, durable builds.
Embrace these practices, and your structures will exemplify strength and longevity.






















